The way Google ranks and indexes content has changed massively over the past ten years. The Google BERT update was one of the most fundamental changes to date. It almost completely altered the way indexing works.
Most changes to the algorithm are fairly minor and occur without much notice. However, the BERT update was a different affair, impacting over 10% of all queries. Let’s take a look at what the Google BERT update involved, how it changed SEO, and what you need to do to make your content rank.
What is the Google BERT Update?
The Google BERT update is a significant advancement in natural language processing (NLP) technology. It stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers. Developed by researchers at Google, it is a state-of-the-art model which aims to make Google’s ranking algorithm work better with actual human speech.
BERT aims to better understand the nuances of our language by processing words in a sentence in relation to its surrounding words. By using a transformer model, it can analyse the full context of a word within a sentence, leading to more accurate language understanding.
By incorporating a bidirectional approach to language understanding, the BERT update has significantly enhanced NLP tasks, such as sentiment analysis, question answering, and text classification. This breakthrough in NLP has paved the way for more accurate and context-aware language models.

If this sounds complicated, don’t worry. You don’t really need to understand the technology of BERT. The thing you need to understand is that BERT is aimed at helping the algorithm understand the way words relate to each other.
In the past, algorithms were less sophisticated and essentially counted the frequency of a given keyword. This isn’t a good reflection of how users actually use keywords.
What is Natural Language Processing?
The key to understanding BERT is understanding what natural language processing (NLP) is. NLP is a field of artificial intelligence focusing on the interaction between computers and humans using natural language. It enables computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language, allowing for more effective communication between machines and humans.
Simply put, BERT is essentially a piece of code that tries to figure out what users actually mean by their search queries in order to match them with the right information.
Think about it like this: The way humans actually talk to each other can be very complex. Many words have different meanings, so context is crucial. Through natural language processing, the Google BERT update is all about understanding the relationships between words.
The flip side of this is that SEO content can read very strangely without NLP. For one thing, one of the algorithm’s main jobs is figuring out what each page on your site is about. This is very difficult if the algorithm can’t understand what each word means.
For example, when we’re speaking or writing, we generally don’t use the same words over and over again. We might use semantic variations or replace these words with pronouns instead.
This doesn’t work if the algorithm can’t understand that some words can mean the same things as each other. As such, the Google BERT update helps reward well-written content on a given topic.
NLP Pre-trained Models
The field of NLP has witnessed significant advancements, particularly with the introduction of pre-trained models. These models act as powerful tools, allowing machines to grasp the complexities of human language and perform various NLP tasks effectively. Some of the popular NLP models that are pre-trained are:
- XLNet: This Google AI model is built upon BERT, addressing some of its limitations by utilising a masked language modelling approach with permutation language modelling.
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): Developed by OpenAI, GPT is known for its impressive ability to generate human-quality text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way.
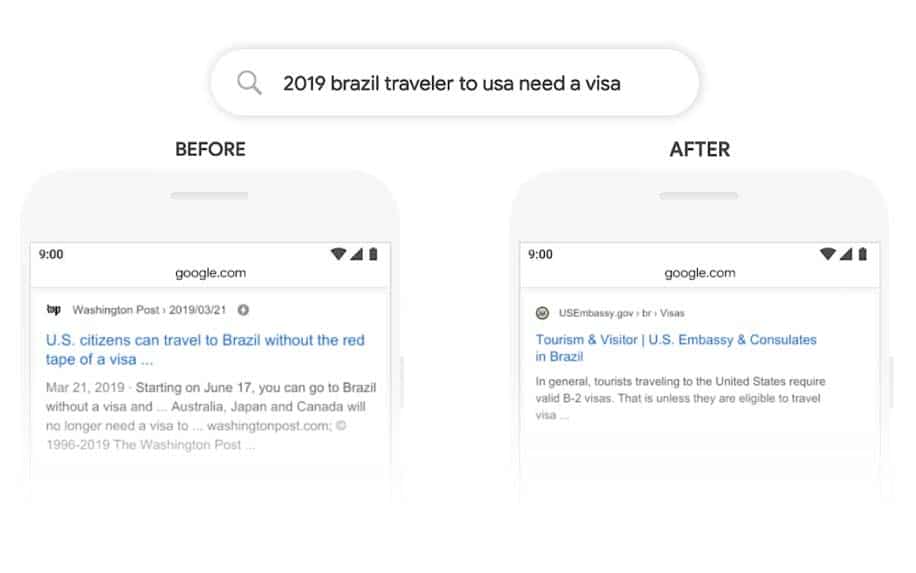
When Did the BERT Update Come into Effect?
BERT was rolled out in October 2019 by Google, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of search engine algorithms. Its impact was visible almost immediately. It revolutionised how search engines interpret user queries and deliver search results by leveraging advanced natural language processing techniques.
If your content were written for search engines rather than to provide value to users, you likely would have seen a huge dip in traffic. By contrast, if you had a track record of publishing interesting and informative content, there’s a good chance you would have seen an uptick, even if you didn’t know much about SEO.
Since its implementation, the BERT update has played a crucial role in improving the accuracy and relevance of search results for users. By understanding the context and intent behind queries, search engines can provide more personalised and precise results, enhancing the overall search experience.
The BERT update has reshaped the way websites approach SEO, emphasising the importance of creating content that meets user needs and addresses search intent. If you adapt your content strategy to align with BERT’s language model, you are more likely to see improvements in your search engine rankings and organic traffic.
So, it’s not an understatement to say that BERT changed SEO forever. Let’s look at how.
What Does the BERT Update Impact?
The Google BERT update essentially marked the end of cramming in keywords and hoping for the best. Once upon a time, if you had a decent website and a high keyword density, your chances of ranking well were pretty high. These days, it’s not so simple.
Remember, BERT is all about understanding how people actually speak. It impacts the way search engines process and understand search queries. This means the Google algorithm became much more sophisticated than simply counting keywords. Instead, it led to more nuanced ways of determining which content is the best.
Search Intent
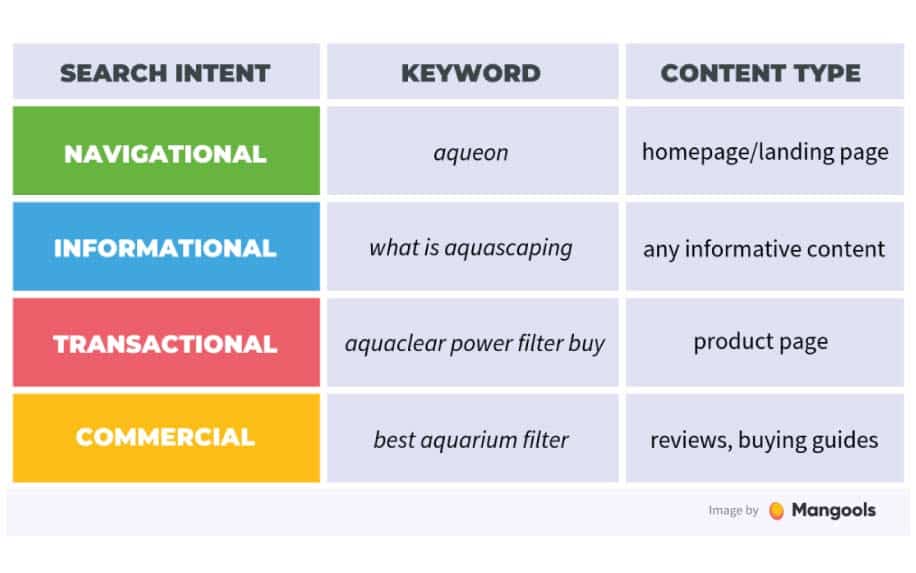
The BERT update brought search intent to the centre of SEO. With a better ability to understand how different words relate to each other, Google also became better at figuring out what users actually want to achieve through search. This is what’s referred to as search intent.
Generally speaking, the search intent of a given query will fall into one of four categories:
- Transactional: Where the user is actively trying to make a particular purchase.
- Commercial Research: Where the user is considering a purchase but needs more information.
- Navigational: Where a user is trying to find a particular website.
- Informational: Where the user is looking for a particular piece of information that is not related to a purchase.
This is crucial, as Google is unlikely to display any content to users which does not match their perceived search intent. We’ll look at how to use this to your advantage a little later.
On-Page SEO

We’ve touched on this already, but BERT also greatly altered the practice of on-page SEO, which plays a crucial role in optimising web pages. If you didn’t know already, on-page SEO is all about writing content that search engines love. Remember, this is not used just to mean getting the keywords in there.
If that’s all you do nowadays, you can hurt your site by getting accused of black-hat SEO strategies, such as keyword stuffing. After the Google BERT update, on-page SEO has become much more user-centric.
What does this mean in practical terms?
The ultimate goal of Google is to match users with the content that provides the most value based on their search intent. While it’s not yet 100% effective at doing this, providing value to users should be the guiding mission of any SEO.
In terms of how you actually write your content, there are a couple of rules of thumb you can keep in mind. The first relates to readability. As the name suggests, this is how easy your content is to read. This can be measured out of 100 using the Flesch Reading Ease Scale. While the exact best readability score varies for different keywords, the higher you can get this, the better.
Similarly, it’s vital to include enough content to answer the user’s query fully. Where once you could provide a few hundred keyword-stuffed words, these days, the most successful content marketing is at least 1,000-2,000 words in length.
The BERT Impact on Other Industries
BERT’s ability to understand complex language has had a profound impact on various fields:
- Search Engines: Search engines, like Google Search, use BERT to deliver more relevant and accurate results, even for complex or nuanced queries.
- Content Creation: BERT can be used to analyse and improve the quality of written content, ensuring clarity, coherence, and engagement.
- Machine Translation: BERT-powered translation models produce more natural and accurate translations, preserving the intended meaning of the original text.
- Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: BERT empowers chatbots and virtual assistants to engage in more natural and meaningful conversations with users.
How to Rank Under the BERT Update
With that in mind, here are a couple of concrete strategies you can implement to maximise your organic traffic after the BERT update.
SERP Research and Understanding Search Intent
We covered the theory behind search intent already, but how do you figure out what a user really wants to achieve? The answer is SERP research. In short, this means checking out what’s already ranking well and learning from what works.
Simply enter your desired target keyword on Google. If the results are mostly product listings, it has a transactional intent. If you see product reviews or comparisons, it’s probably commercial research. The goal here is to figure out what kind of content performs the best and do it better yourself.
User’s Question Answering
Responding to user questions is an excellent SEO strategy. For one thing, these questions make it easy to match valuable content to the search intent. For another, they’re a great way to appear in “Featured Snippets” and “People also ask” boxes.
Where can you find good questions to write content around?
As part of your keyword research, look for opportunities with words like who, what, when, and why. Even if you can’t find any, think about ways to use these phrases in subheadings with your target keyword. For instance, “What is KEYWORD?” or “Why is KEYWORD important?”
To find good questions to write content around, you can use various tools and resources, such as:
- Keyword Research Tools, like Google Keyword Planner and SEMrush
- Forums and Community Platforms, like Reddit and Quora
- Social Media Platforms, like X/Twitter, Facebook, and LinkedIn
- Q&A Websites, like Yahoo Answers, Stack Exchange, and Answer The Public
Social media platforms are useful for discovering trending topics and popular questions among users. By monitoring conversations, hashtags, and user interactions, you can uncover relevant questions to address in your content and attract a wider audience.
Q&A websites are dedicated platforms where users ask questions on various topics. You can utilise them to identify common questions, concerns, and interests within your niche and create comprehensive answers that cater to user needs.
The Future of BERT
Since its introduction, BERT has become a cornerstone of NLP research and development. It is open source, and this nature has allowed researchers and developers to explore its potential in various applications, pushing the boundaries of human-computer interaction. As AI continues to evolve, BERT is expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of how we interact with machines and navigate the vast world of information.
In the realm of SEO, BERT will likely shape the way websites approach content creation and optimisation. The future of BERT also includes advancements in machine learning and deep learning techniques to enhance the model’s language understanding capabilities further.
Looking Ahead
As Google continues to refine and expand BERT’s capabilities, the future of search promises to be more intuitive, contextually aware, and user-centric. Digital marketers and businesses must adapt to these changes by prioritising user experience, relevance, quality in their content, and optimisation strategies.
By embracing BERT and its advancements in natural language understanding, marketers can position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive digital landscape.
In conclusion, the Google BERT update represents a significant leap forward in NLP, paving the way for a future where machines can understand and respond to human language with greater sophistication and nuance.
For help and advice on SEO strategy or any other kind of digital marketing, why not reach out to our team of experts today?